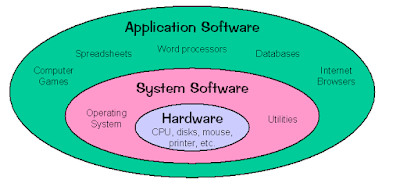
Computer Network Topologies:-
A Network Topology is the way PC frameworks or system hardware associated with one another. Topologies may characterize both physical and coherent part of the system. Both sensible and physical topologies could be same or diverse in a same system.
Point-to-point :-
Point-to-point systems contains precisely two hosts (PC or switches or switches or servers) joined consecutive utilizing a solitary bit of link. Regularly, the less than desirable end of one host is associated with sending end of the flip side and bad habit versa.If the hosts are joined point-to-point coherently, then may have various middle of the road gadgets. Be that as it may, the end hosts are unconscious of hidden system and see one another as though they are joined straightforwardly.
Bus Topology:-
As opposed to point-to-point, in transport topology all gadget offer single correspondence line or link. All gadgets are associated with this common line. Transport topology may have issue while m mineral than one hosts sending information in the meantime. In this way, the transport topology either utilizes CSMA/CD innovation or perceives one host has Bus Master to fathom the issue. It is one of the straightforward types of systems administration where a disappointment of a gadget does not influence t he others. Be that as it may, disappointment of the common correspondence line make every single other gadget fail.Both closures of the mutual channel have line eliminator. The information is sent in one and only course and when it achieves the compelling end, the eliminator expels the information from the line.
Star Topology:-
All hosts in star topology are joined with a focal gadget, known as Hub gadget, utilizing a point-to-point association. That is, there exists a point to point association in the middle of hosts and Hub. The center point gadget can be Layer-1 gadget (Hub/repeater) or Layer-2 gadget (Switch/Bridge) or Layer-3 gadget (Router/Gateway).As in transport topology, center point goes about as single purpose of disappointment. In the event that center falls flat, integration of all hosts to every other host fizzles. Each correspondence happens between hosts, experiences Hub just. Star topology is not costly as to unite one more host, stand out link is obliged and setup is basic.
Ring Topology:-
In ring topology, every host machine interfaces with precisely two different machines, making a roundabout system structure. At the point when one host tries to convey or send message to a host which is not nearby it, the information goes through every middle of the road host. To unite one more host in the current structure admini strator may require one and only all the more additional cable.Failure of any host brings about disappointment of the entire ring. Accordingly every association in the ring is purpose of disappointment. There exists systems which utilizes one more reinforcement ring.
Network Topology:-
In this kind of topology, a host is associated with maybe a couple or more than two hosts. This topology may have hosts having point-to-guide association toward each different has or might likewise have has which are having point to direct association toward few hosts only.Hosts in Mesh topology additionally function as hand-off for different hosts which don't have direct point-to-point joins. Network innovation comes into two flavors:
· Full Mesh:-
All hosts have a point-to-direct association toward each other host in the system. Consequently for each new host n(n-1)/2 links (association) are needed. It gives the most dependable system structure among all system topologies.
· Partially Mesh:-
Not all hosts have point-to-guide association toward each other host. Hosts associate with each otherin some subjectively mold. This topology exists where we have to give unwavering quality to some host though others are not in that capacity fundamental.
Tree Topology :-
Otherwise called Hierarchical Topology is the most widely recognized type of system topology being used present day. This topology mirrors as broadened Star Topology and acquires properties of Bus topology.This topology partitions the system into various levels/layers of system. For the most part in LANs, a system is bifurcated into three sorts of system gadgets. The least most is access-layer where user‟s PC are appended. The center layer is known as dissemination layer, which acts as middle person between upper layer and lower layer. The most elevated most layer is known as Core layer, and is main issue of the system, i.e. foundation of the tree from which all hubs fork.All neighboring hosts have point-to-point association between them. Like transport topology, if the root goes down, the whole system endures. In spite of the fact that it is not the single purpose of disappointment. Each association serves as purpose of disappointment, coming up short of which partitions the system into inaccessible section et cetera.
Daisy Chain :-
This topology join every one of its has in a direct manner. Like Ring topology, all hosts in this topology are joined with two hosts just, aside from the end has. That is if the end has in Daisy Chain are joined then it speaks to Ring topology.Each connect in Daisy chain topology speaks to single purpose of disappointment. Each connection disappointment parts the system into two section. Each middle host fills in as transfer for its quick has.
Hybrid Topology:-
A system structure whose outline contains more than one topology is said to be Hybrid Topology. Half and half topology acquires benefits and negative marks of all the consolidating topologies.The above picture speaks to a discretionarily Hybrid topology. The joining topologies may contain traits of Star, Ring, Bus and Daisy-chain topologies. Most WANs are associated by method for double Ring topology and systems joined with them are for the most part Star topology systems. Web is the best illustration of biggest Hybrid top.
A Network Topology is the way PC frameworks or system hardware associated with one another. Topologies may characterize both physical and coherent part of the system. Both sensible and physical topologies could be same or diverse in a same system.
Point-to-point :-
Point-to-point systems contains precisely two hosts (PC or switches or switches or servers) joined consecutive utilizing a solitary bit of link. Regularly, the less than desirable end of one host is associated with sending end of the flip side and bad habit versa.If the hosts are joined point-to-point coherently, then may have various middle of the road gadgets. Be that as it may, the end hosts are unconscious of hidden system and see one another as though they are joined straightforwardly.
Bus Topology:-
As opposed to point-to-point, in transport topology all gadget offer single correspondence line or link. All gadgets are associated with this common line. Transport topology may have issue while m mineral than one hosts sending information in the meantime. In this way, the transport topology either utilizes CSMA/CD innovation or perceives one host has Bus Master to fathom the issue. It is one of the straightforward types of systems administration where a disappointment of a gadget does not influence t he others. Be that as it may, disappointment of the common correspondence line make every single other gadget fail.Both closures of the mutual channel have line eliminator. The information is sent in one and only course and when it achieves the compelling end, the eliminator expels the information from the line.
Star Topology:-
All hosts in star topology are joined with a focal gadget, known as Hub gadget, utilizing a point-to-point association. That is, there exists a point to point association in the middle of hosts and Hub. The center point gadget can be Layer-1 gadget (Hub/repeater) or Layer-2 gadget (Switch/Bridge) or Layer-3 gadget (Router/Gateway).As in transport topology, center point goes about as single purpose of disappointment. In the event that center falls flat, integration of all hosts to every other host fizzles. Each correspondence happens between hosts, experiences Hub just. Star topology is not costly as to unite one more host, stand out link is obliged and setup is basic.
Ring Topology:-
In ring topology, every host machine interfaces with precisely two different machines, making a roundabout system structure. At the point when one host tries to convey or send message to a host which is not nearby it, the information goes through every middle of the road host. To unite one more host in the current structure admini strator may require one and only all the more additional cable.Failure of any host brings about disappointment of the entire ring. Accordingly every association in the ring is purpose of disappointment. There exists systems which utilizes one more reinforcement ring.
Network Topology:-
In this kind of topology, a host is associated with maybe a couple or more than two hosts. This topology may have hosts having point-to-guide association toward each different has or might likewise have has which are having point to direct association toward few hosts only.Hosts in Mesh topology additionally function as hand-off for different hosts which don't have direct point-to-point joins. Network innovation comes into two flavors:
· Full Mesh:-
All hosts have a point-to-direct association toward each other host in the system. Consequently for each new host n(n-1)/2 links (association) are needed. It gives the most dependable system structure among all system topologies.
· Partially Mesh:-
Not all hosts have point-to-guide association toward each other host. Hosts associate with each otherin some subjectively mold. This topology exists where we have to give unwavering quality to some host though others are not in that capacity fundamental.
Tree Topology :-
Otherwise called Hierarchical Topology is the most widely recognized type of system topology being used present day. This topology mirrors as broadened Star Topology and acquires properties of Bus topology.This topology partitions the system into various levels/layers of system. For the most part in LANs, a system is bifurcated into three sorts of system gadgets. The least most is access-layer where user‟s PC are appended. The center layer is known as dissemination layer, which acts as middle person between upper layer and lower layer. The most elevated most layer is known as Core layer, and is main issue of the system, i.e. foundation of the tree from which all hubs fork.All neighboring hosts have point-to-point association between them. Like transport topology, if the root goes down, the whole system endures. In spite of the fact that it is not the single purpose of disappointment. Each association serves as purpose of disappointment, coming up short of which partitions the system into inaccessible section et cetera.
Daisy Chain :-
This topology join every one of its has in a direct manner. Like Ring topology, all hosts in this topology are joined with two hosts just, aside from the end has. That is if the end has in Daisy Chain are joined then it speaks to Ring topology.Each connect in Daisy chain topology speaks to single purpose of disappointment. Each connection disappointment parts the system into two section. Each middle host fills in as transfer for its quick has.
Hybrid Topology:-
A system structure whose outline contains more than one topology is said to be Hybrid Topology. Half and half topology acquires benefits and negative marks of all the consolidating topologies.The above picture speaks to a discretionarily Hybrid topology. The joining topologies may contain traits of Star, Ring, Bus and Daisy-chain topologies. Most WANs are associated by method for double Ring topology and systems joined with them are for the most part Star topology systems. Web is the best illustration of biggest Hybrid top.